Preparation and Application of Fumed Silica
Fumed silica, is a high-purity, amorphous white powder. It is a unique ultra-fine nano-scale material in the industry. It has the characteristics of small particle size, ultra-high specific surface area and high purity. It exhibits excellent dispersibility, reinforcement, thickening, thixotropy and other properties; it is widely used in coatings, rubber, resins, adhesives, electronic power, insulation, construction and other fields, and is known as "industrial monosodium glutamate".
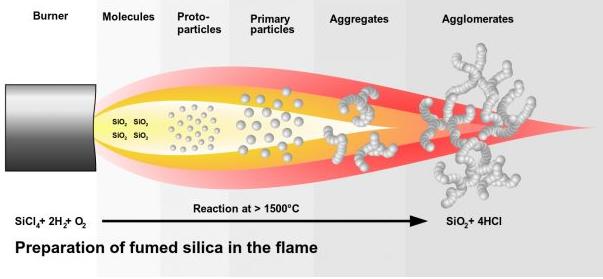
Fumed silica is produced by the use of silicon chloride-silicon tetrachloride for high-temperature gas-phase hydrolysis in a hydrogen-oxygen flame, and the flame temperature needs to be greater than 1000°C. . Its reaction formula and production process can be seen in the following figure for reference.
Primary silica particles: The initial state of silica particles in the free radical reaction, also called primary particles, about 7-40 nanometers.
Aggregate: Intermediate particle morphology, aggregates, about 100-500 nanometers, also ideal after good dispersion.
Agglomeration: Attachment to the collective. Morphology of fumed silica under natural conditions
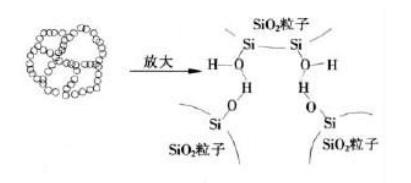
Since the surface of fumed silica has a large number of hydroxyl groups, these hydroxyl groups will generate hydrogen bonds between the aggregates of fumed silica. When they are fully dispersed in the liquid system, a three-dimensional network structure of silica will be formed, as follows As shown in the figure:
Preparation and Application of Fumed Silica

Fumed silica, is a high-purity, amorphous white powder. It is a unique ultra-fine nano-scale material in the industry. It has the characteristics of small particle size, ultra-high specific surface area and high purity. It exhibits excellent dispersibility, reinforcement, thickening, thixotropy and other properties; it is widely used in coatings, rubber, resins, adhesives, electronic power, insulation, construction and other fields, and is known as "industrial monosodium glutamate".
Fumed silica is produced by the use of silicon chloride-silicon tetrachloride for high-temperature gas-phase hydrolysis in a hydrogen-oxygen flame, and the flame temperature needs to be greater than 1000°C. . Its reaction formula and production process can be seen in the following figure for reference.
Primary silica particles: The initial state of silica particles in the free radical reaction, also called primary particles, about 7-40 nanometers.
Aggregate: Intermediate particle morphology, aggregates, about 100-500 nanometers, also ideal after good dispersion.
Agglomeration: Attachment to the collective. Morphology of fumed silica under natural conditions
Since the surface of fumed silica has a large number of hydroxyl groups, these hydroxyl groups will generate hydrogen bonds between the aggregates of fumed silica. When they are fully dispersed in the liquid system, a three-dimensional network structure of silica will be formed, as follows As shown in the figure:
